Below is a selection of research projects I have been working on or supervising in the past years at The Hague University of Applied Sciences.
Highlighted projects listed first.
Public Dialogues #goodtalk

Changes in society invariably lead to feelings of discomfort, tensions and social unrest, also in our present time. Media, and social media in particular, quickly and effectively make such feelings publicly visible and therefore have a magnifying effect on the sentiments in society: tweeting your opinion is a piece of cake, just like reacting to opinions, but a dialogue will not easily get started and polarization is imminent.

The project has a duration of two years, starts April 1, 2019, and is co-funded with a research grant from SIA (RAAK-Publiek). The project team consists of ca. 30 professionals from the participating organisations, a mix of researchers, designers, and professionals in the involved metropolitan neighbourhoods.
Various metropolitan neighbourhoods manifest, for a long time already, tensions between citizens and between citizens and professionals and municipal officials in the neighbourhood. Frequent incidents point out discomposure, disgruntlement, and polarisation. Inhabitants experience problems due to differences in values and opinions about the design and use of public space and co-inhabiting the neighbourhood; these tensions sometimes lead to violent behaviour and undisguised racism. Relationships with public organisations get strained and ruled by sentiments of mistrust. The result is that citizens feel a distance to authorities and communication is weakened even further.
These tense relationships often have a background in public values and public dialogues about values. It appears to be difficult, when there are feelings of unrest and uncertainty, to look beyond one’s own values and interests and to participate respectfully in a public dialogue about shared interests and public values. Municipalities, and neighbourhood managers in particular, struggle with increasing manifestations of polarisation.
A public dialogue requires specific social skills, from both citizens and professionals. In this project, departing from a knowledge base in philosophy, a methodology is created and tested that empowers neighbourhood managers to lead people in a dignified public dialogue, both in local conversations and on social media, through special attention for – and development of – dialogue skills. We do this in four work packages:
- Formulate a model of skills for public dialogues;
- Operationalise the model in practical guidelines for how to guide dialogues;
- Design and experimental evaluation of dialogical forms of social media;
- Evaluation, quality assessment and effect analysis of online and local dialogues.
Artificial Intelligence in Public Spaces
The municipality of The Hague is planning the installation of a smart city infrastructure in Scheveningen. In this research project we collaborated with the municipality and local entrepreneurs to conceptualise new services that make use of this outdoor infrastructure and artificial intelligence. The project was financially supported with a SIA KIEM grant.
 This research project was flanked by numerous student projects that yielded both research results and design concepts.
This research project was flanked by numerous student projects that yielded both research results and design concepts.
Virtual Reality for citizen participation in urban development
 For the revamp of a local park, the municipality of The Hague invited local residents to participate in its design. This process was supported with VR technology. Our research aimed to measure the effectiveness of the technology and this participatory design approach to increase citizen engagement.
For the revamp of a local park, the municipality of The Hague invited local residents to participate in its design. This process was supported with VR technology. Our research aimed to measure the effectiveness of the technology and this participatory design approach to increase citizen engagement.
Creating Awareness in Motorists about Emission Consequences
 How do we make motorists more aware of the consequences of vehicle emission? Naming and shaming, or empowerment to change? This project aimed to find the best approach for individual needs.
How do we make motorists more aware of the consequences of vehicle emission? Naming and shaming, or empowerment to change? This project aimed to find the best approach for individual needs.
Prototype created by Ismaël Harraou.
Theme Investigation in Design Thinking
 This project aimed at developing methodology for theme investigation, which is a key activity in reframing complex problems in processes of design thinking. The project involved a long-term study of over 10 case studies, in the domain of social design, in which the research team engaged in co-design with stakeholders to reframe complex problems in order to find novel solutions. The research has identified best practices and resulted in a set of tools to support theme investigation.
This project aimed at developing methodology for theme investigation, which is a key activity in reframing complex problems in processes of design thinking. The project involved a long-term study of over 10 case studies, in the domain of social design, in which the research team engaged in co-design with stakeholders to reframe complex problems in order to find novel solutions. The research has identified best practices and resulted in a set of tools to support theme investigation.
Street Speed Trap
 This project is about citizen empowerment: giving citizens a tool to measure speeding traffic in their street. The objective is not to take over policing tasks, but to gather evidence that action is needed.
This project is about citizen empowerment: giving citizens a tool to measure speeding traffic in their street. The objective is not to take over policing tasks, but to gather evidence that action is needed.
Prototypes created by Annemarie Vermaesen and Felix Cuellar.
Social media restructured
 Current social media are designed around timelines: they present discussion in chronological order only. This project aimed to design alternative ways to present posts on social media that can improve the quality of discussions.
Current social media are designed around timelines: they present discussion in chronological order only. This project aimed to design alternative ways to present posts on social media that can improve the quality of discussions.
Prototypes created by Huy Trinh and Diko van der Meer.
Slow Mail
With the introduction of email, sending messages and letters has nog only become easier, but also faster. In general, we experience this as an optimisation and improvement of the physical letters we used to send. yet, sending mail on paper, in an envelope, certainly had its charm that we rarely experience any longer. This project is a search for new forms of communication that function with modern technology but retain the type of charm that hand-written paper post possessed. It appears to be difficult to let go of existing metaphors and known forms of interaction.
A concept for a modern slow mail service was created by Tim Davids.
Embedded Park Easy
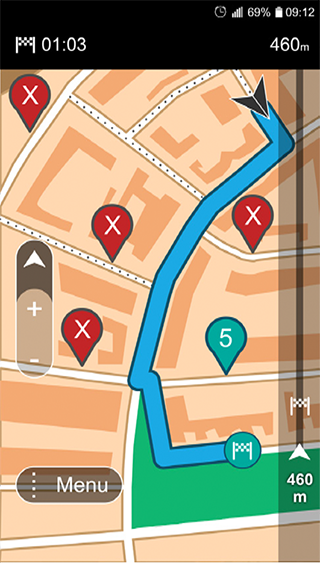 Finding a parking garage is easy with today’s car navigation systems, but finding a parking lot in the street is a challenge. This project explores the required technology and the optimal interface design for a mobile app that helps you find a free spot to park.
Finding a parking garage is easy with today’s car navigation systems, but finding a parking lot in the street is a challenge. This project explores the required technology and the optimal interface design for a mobile app that helps you find a free spot to park.
Prototypes created by Brinsley Ramtahalsing, Kevin Netteb, and Sinthujan Jeyakumar.
Smart Spui, Den Haag
 The main crossing in the centre of The Hague is characterised by a lack of traffic rules, with public transport, taxis and bikes passing through the crowd of pedestrians. This project took a leap forward and conceptualised how autonomous public transport, without drivers, can communicate its intentions to pedestrians.
The main crossing in the centre of The Hague is characterised by a lack of traffic rules, with public transport, taxis and bikes passing through the crowd of pedestrians. This project took a leap forward and conceptualised how autonomous public transport, without drivers, can communicate its intentions to pedestrians.
Prototype created by Elize de Kuijper.
Message on the Spot
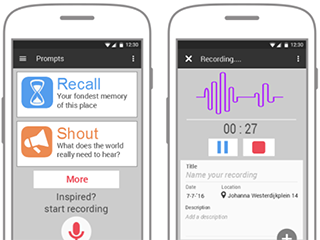 Current technology offers opportunities to deploy location-awareness in mobile apps. This project explored a range of design concepts for services that aim to bring people together in novel ways, using location-awareness and cultural content to foster serendipity and chance encounters.
Current technology offers opportunities to deploy location-awareness in mobile apps. This project explored a range of design concepts for services that aim to bring people together in novel ways, using location-awareness and cultural content to foster serendipity and chance encounters.
Prototypes created by Jim Bemelmans, Brent Rundberg, and Pitnaree Krachangwong.
Citizen-Pro
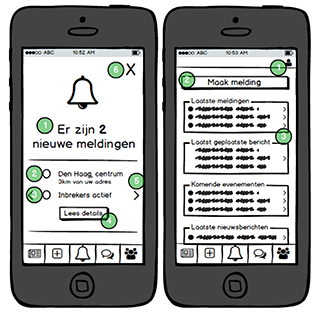 The app designed in this project allows citizens to map such issues, ranging from social incidents to required maintenance and desired changes. Both professionals and citizens can benefit from becoming aware of the issues at stake in a neighbourhood and discussing them publicly.
The app designed in this project allows citizens to map such issues, ranging from social incidents to required maintenance and desired changes. Both professionals and citizens can benefit from becoming aware of the issues at stake in a neighbourhood and discussing them publicly.
Prototypes were created by: Danique Valstar, Jeroen Diks, Mia Henkels, Boy Versteeg, Daniel Ramirez Torres, Gino Aldewereld, and Hamoen Ghafelehbashi.
Your Own Neighbourhood
 How can citizens be motivated to be more engaged and participate in developments of the public areas in their neighbourhood? This project created new service concepts for the municipality of The Hague to approach citizens that usually do not participate, in a motivating way.
How can citizens be motivated to be more engaged and participate in developments of the public areas in their neighbourhood? This project created new service concepts for the municipality of The Hague to approach citizens that usually do not participate, in a motivating way.
Service prototypes created by Roel van Adrichem, Jeroen Dijkstra, Andrew Lekahena, Brent Rundberg, Gino Aldewereld, Romy Koch, Samira El Messaoudi, Ananta Mulyono, Rick van den Broek, Tim Davids, Arjan Elschot, Ismael Harraou, Gerhard Kraaijenoord, Suzanne van den Berg, Dominique Chalabalaki, Raisa de Koning, Nadesh Ligthart, Jim Bemelmans, Texas de Bruin, Kelly Ferwerda, Boas van Olden, Tessa Guijt, Diko van der Meer, Huy Trinh, Ria Verleg, Tilly Brito, Midge Hazewinkel, Norvin Mercelina, Adjay Ramkhelawan, Arjen Holleman, Justin Hundman, David de Jonge, and Boy de Wit.
Interactive Technology in the Social Life of Elderly
 Elderly are often physically challenged and as a result socially limited. This project explored the social needs of elderly, e.g. in fighting loneliness, and the design requirements this imposes on communication tools that could support and alleviate them and their social circle.
Elderly are often physically challenged and as a result socially limited. This project explored the social needs of elderly, e.g. in fighting loneliness, and the design requirements this imposes on communication tools that could support and alleviate them and their social circle.
Concepts developed by Hussein Houssein, Ferdi Mac Gillavry, Bas Hellings, Dennis Weijsenfeld, Cor Hortensius, Karin Valstar, Frans Huigen, Justin van der Vlies, Daniëlle Aartsen, and Joris Giesbers.
Services and prototypes created by Minji Jung, Sarah Lopez Chavarria, Margot Mollerus, Sybren Burghout, Siyun Hwang, Ue Jun Kim, Casper Piket, Nahwin Chedoe, Jerry Koers, and Faisal Moulay Ahmed.
Services in Mariahoeve
 The Mariahoeve district of The Hague request the design of a new set of services to stimulate employment and increase social inclusion in its neighbourhood. In this project, students and researchers worked together with practitioners to conceptualise new services: Mariahoeve Storytelling Platform and Mariahoeve Pick-up Service. The latter service was conceptualised, implemented, and put in practice by Leonie Flin.
The Mariahoeve district of The Hague request the design of a new set of services to stimulate employment and increase social inclusion in its neighbourhood. In this project, students and researchers worked together with practitioners to conceptualise new services: Mariahoeve Storytelling Platform and Mariahoeve Pick-up Service. The latter service was conceptualised, implemented, and put in practice by Leonie Flin.

Development Aid Insights
 The Ministry of Foreign Affairs aims to publish financial data from IATI on aid programmes in correlation to data from the World Bank, to give insight into indicators of development (e.g. birth rates, death rates, epidemic spread, etc.) and therefore into the effectiveness of the aid programmes. This project explored the possible interfaces for an online platform for the support of policymakers, aid organisations, journalists, and politicians.
The Ministry of Foreign Affairs aims to publish financial data from IATI on aid programmes in correlation to data from the World Bank, to give insight into indicators of development (e.g. birth rates, death rates, epidemic spread, etc.) and therefore into the effectiveness of the aid programmes. This project explored the possible interfaces for an online platform for the support of policymakers, aid organisations, journalists, and politicians.
Special Welfare Online
 Applying for special welfare is often hard. Not just because it is difficult emotionally, but also because the process is cumbersome. This project, in collaboration with Centric, aimed to redesign that process and create better online solutions, to lower the thresholds.
Applying for special welfare is often hard. Not just because it is difficult emotionally, but also because the process is cumbersome. This project, in collaboration with Centric, aimed to redesign that process and create better online solutions, to lower the thresholds.
Lost and Found
 The municipality of The Hague commissioned this project to design a new online platform to reunite citizens with their lost properties that have been found, but are not yet retrieved. The new platform aims to reduce costs of storage and communication.
The municipality of The Hague commissioned this project to design a new online platform to reunite citizens with their lost properties that have been found, but are not yet retrieved. The new platform aims to reduce costs of storage and communication.
Below is a selection of research projects I have worked on or supervised, between 2006 and 2011, at the University of Madeira and at the Madeira Interactive Technologies Institute.
Highlighted projects listed first.
Remote Presence
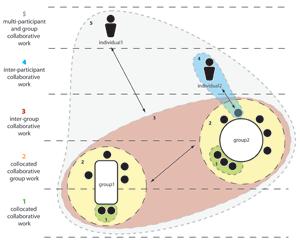 Clinton Jorge worked on his graduation project in the MSc in Computer Science at the University of Madeira in a collaboration with Alcatel-Lucent Bell Laboratories, Antwerp.
Clinton Jorge worked on his graduation project in the MSc in Computer Science at the University of Madeira in a collaboration with Alcatel-Lucent Bell Laboratories, Antwerp.
The objective of this research project was to design and prototype a collaboration environment, based on multi-touch capable, personal devices such as iPads and iPhones, that affords an engaging and effective experience to participants involved in distributed meetings or presentations. The main features of the envisioned environment are:
- Ubiquitous meeting and presentation management tools
- Intuitive and instantly shared interactivity with content, media, and devices
- Synchronous, multi-modal communication between participants
Research question: Can this collaboration environment improve inter-participant interaction and involvement?
The initial phase of this project targets an iPad tool to allow interactions with a presentation to be communicated to a remote audience. We will design the interaction and measure its effectiveness in inducing correct understanding in the audience and engagement with the presentation.
Madeira Life
 Today, most people regard the Internet as the foremost source of information in their lives. The Internet is where we make contact, with friends, with organisations and events, with products and places. We book and reserve, buy or sell real products and services. In a way, we could say that the Internet is becoming an interface to the real world. Madeira Life is the ultimate portal of Madeira: it offers the residents and visitors of Madeira a highly interactive, social network with mobile and location-aware access. It is the place to share photos, video, audio, and text, and connect this content to where you are, as author or audience. Read blogs that were written where you are, hear stories and see videos about the place, or simply get information about sales and promotions nearby. You can get it right there, right now. Madeira Life will accompany you all over the island and be your best link with the world.
Today, most people regard the Internet as the foremost source of information in their lives. The Internet is where we make contact, with friends, with organisations and events, with products and places. We book and reserve, buy or sell real products and services. In a way, we could say that the Internet is becoming an interface to the real world. Madeira Life is the ultimate portal of Madeira: it offers the residents and visitors of Madeira a highly interactive, social network with mobile and location-aware access. It is the place to share photos, video, audio, and text, and connect this content to where you are, as author or audience. Read blogs that were written where you are, hear stories and see videos about the place, or simply get information about sales and promotions nearby. You can get it right there, right now. Madeira Life will accompany you all over the island and be your best link with the world.
The project was co-funded by ZON Multimedia and the +Conhecimento fund (Madeira regional government) and had a total budget of 633 k€.
Multi-touch, multi-user collaboration on a tabletop
 Elvio Pita’s graduation project in the MSc in Computer Science at the University of Madeira aimed to develop a application for collaborative editing of documents on an interactive tabletop.
Elvio Pita’s graduation project in the MSc in Computer Science at the University of Madeira aimed to develop a application for collaborative editing of documents on an interactive tabletop.
The objective of this MSc project was to design and prototype a multi-user application that provides multi-touch interaction to shared media. This application provides collocated participants of a meeting a way to interact with all content on the table. The application is designed for a tabletop interface and allows users to have shared interactions with documents that are presented on the tabletops. The tabletop becomes an enhanced meeting table where the boundary between paper and digital documents fades.
Touch’n’Sketch
 Hugo Vieira’s graduation project in the MSc in Computer Science at the University of Madeira aimed to develop a touch+pen interaction for a CASE tool.
Hugo Vieira’s graduation project in the MSc in Computer Science at the University of Madeira aimed to develop a touch+pen interaction for a CASE tool.
The objective of this MSc graduation project was to find the most useful and usable multi-touch (finger) interactions with pen-enabled interactive screens. The hypothesis is that smart combinations of finger and pen interactions provide more efficient and accurate interactions than just finger or just pen interactions. In this project we design these interactions and build a prototype in order to test and proof their usability and effectiveness through user testing. The application domain we selected for the project is a CASE tool (Computer-Aided Software Engineering) that allows sketching so-called Human-Activity Models.
Then’n’Now
 Pedro Teixeira’s graduation project in the MSc in Computer Science at the University of Madeira aimed to make old photographs available on mobile devices and, making use of GPS functionality, helping the user to find the exact location where these photographs were taken.
Pedro Teixeira’s graduation project in the MSc in Computer Science at the University of Madeira aimed to make old photographs available on mobile devices and, making use of GPS functionality, helping the user to find the exact location where these photographs were taken.
The designed and developed application targets Android devices and offers three modes for locating photographs. In a map view, the user finds an overview of nearby located photographs that are accessible through the online archive. Using the map, one can navigate to this location. Once in the neighbourhood, the photograph can be seen in the augmented reality view (using the devices in the upright position), which places the photograph in an iconic representation in the 3D space registered on the device using its camera. When the user is really near the photograph’s location, the image will ‘snap’ to the display in semi-transparency and the user can move to the exact location where the camera’s image and photograph overlay, showing ‘then’ and ‘now’ in a matched view.
SINAIS: Service Innovations through social Networks, context Awareness and Interaction for Sustainability
HCI is a multi-disciplinary field in which sustainability research is an emerging topic of interest. In this project, motivational theories and research through design processes are applied to understand, motivate, support and encourage sustainable behaviour. The focus is on two domains: Home (referring to resource consumption of electricity, gas and water in residences) and Transport (referring to travel and commuting behaviour). The key enabling technologies and methods that will be deployed in this project include social network analysis, advanced sensors and data processing algorithms, and interaction design. The overall goal of the work is to weave these threads together, to meld sensor technologies and human-computer interaction design with the motivating power of social networks in order to achieve significant changes in the consumption behaviour of communities.
The project is executed at Madeira-ITI and at the HCII in Pittsburgh. It is funded by FCT (Portuguese Ministry of Science and Higher Education) with a budget of 573 k€ for the Portuguese part of the project.
Culture’s4us
This is an MSc graduation project by two students, Gustavo Fernandes in the Master of Computer Science and Gonçalo Luís in the Master of Telecommunications, both at the University of Madeira. The general objective of this project is to define and develop a new mode of communicating with tourists, pre-travel as well as during their stay at the destination. To achieve this, the project develops a web-based communication platform that is accessible from desktop computers but also targeted specifically at modern mobile devices such as cell phones and pocket computers.
 The prototype developed in the project enables fully automatic geotagging of pictures taken by tourists using their mobile phones and uploaded to a server that tracks their travel over the island of Madeira.
The prototype developed in the project enables fully automatic geotagging of pictures taken by tourists using their mobile phones and uploaded to a server that tracks their travel over the island of Madeira.
Below is a selection of research projects I have worked on or supervised, between 1993 and 2006, at Eindhoven University of Technology.
Highlighted projects listed first.
CoDesKs: Management and Communication of Distributed Conceptual Design Knowledge in the Building and Construction Industry
 The objective of this research project is to develop a technological and organisational framework for the management and communication of conceptual design knowledge in a distributed environment. This framework allows designers to model their expertise and use it in computational design reasoning; it also allows them to share this expertise, enabling them to use each other’s design knowledge and reasoning mechanisms. The project has developed the technology and the organisational aspects that are required for designers to build up a common, but distributed, design knowledge base. Technologically, the result is a framework that implements a distributed object model with object-level versioning.
The objective of this research project is to develop a technological and organisational framework for the management and communication of conceptual design knowledge in a distributed environment. This framework allows designers to model their expertise and use it in computational design reasoning; it also allows them to share this expertise, enabling them to use each other’s design knowledge and reasoning mechanisms. The project has developed the technology and the organisational aspects that are required for designers to build up a common, but distributed, design knowledge base. Technologically, the result is a framework that implements a distributed object model with object-level versioning.
 This project was, in the first year, executed at the Instituto Superior Técnico (Technical University of Lisbon, Portugal) and co-financed by Eindhoven University of Technology and the Portuguese Ministry of Science and Education.
This project was, in the first year, executed at the Instituto Superior Técnico (Technical University of Lisbon, Portugal) and co-financed by Eindhoven University of Technology and the Portuguese Ministry of Science and Education.
The Digital Dormer: online building permits
 Dormers are the most required modifications to peoples’ homes in The Netherlands. A city like Rotterdam, yearly handles about 300 requests for building permits concerning dormers. The costs of dormers are relatively low and therefore the administrative costs will be relatively high. The aim of the project is to improve the quality of the submitted requests and to streamline the process of checking the requests. This is achieved through a website where citizens can ‘design’ their dormer online and provide all necessary information to automatically check for all building codes. The site also provides additional advise to the citizen regarding the construction, insulation, daylight, ventilation, etc. of the dormer. The citizen using the site can then submit the application for the building permit online. Finally, the construction project can be entered into an online tender, where local contractors can bid for the project.
Dormers are the most required modifications to peoples’ homes in The Netherlands. A city like Rotterdam, yearly handles about 300 requests for building permits concerning dormers. The costs of dormers are relatively low and therefore the administrative costs will be relatively high. The aim of the project is to improve the quality of the submitted requests and to streamline the process of checking the requests. This is achieved through a website where citizens can ‘design’ their dormer online and provide all necessary information to automatically check for all building codes. The site also provides additional advise to the citizen regarding the construction, insulation, daylight, ventilation, etc. of the dormer. The citizen using the site can then submit the application for the building permit online. Finally, the construction project can be entered into an online tender, where local contractors can bid for the project.
Multi Agent Systems for Collaborative Design
The objective of this PhD research project by Jakob Beetz is to facilitate the use of external knowledge from various resources and domains in a building design project. At design time, the designer has to take many external factors into consideration that affect the quality and performance of the building – especially in the early phases of the design. Unfortunately though, much of these additional factors are not accessible or take a long time to be calculated.
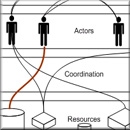 This project combines product modelling standards (IFC) and semantic web technology (OWL) with multi-agent technology to develop a framework for agents that represent expert knowledge from a particular discipline, such as an HVAC consultant. Agents can also be developed to represent building components that are required to manifest certain behaviour in a building, e.g. a ventilation unit. In both case, the agent is an autonomous software objects that can be given a task in a certain context, such as making sure that the required performance can be achieved in the design.
This project combines product modelling standards (IFC) and semantic web technology (OWL) with multi-agent technology to develop a framework for agents that represent expert knowledge from a particular discipline, such as an HVAC consultant. Agents can also be developed to represent building components that are required to manifest certain behaviour in a building, e.g. a ventilation unit. In both case, the agent is an autonomous software objects that can be given a task in a certain context, such as making sure that the required performance can be achieved in the design.
Jacob received his PhD in 2009 and is now professor at Aachen University.
PAIS organisation
 In the PAIS organisation, six Dutch national standardisation initiatives for the building and construction sector have been brought together. The objective of the PAIS organisation is to realise a coherent information structure for these standardisation projects, ensuring their interoperability for the long term. The development of this information structure is necessary to allow the building and construction sector to make optimal use of the possibilities of ICT, particularly in the communication between project partners. The validity and efficacy of the standardisation projects are subject to research in special validation projects.
In the PAIS organisation, six Dutch national standardisation initiatives for the building and construction sector have been brought together. The objective of the PAIS organisation is to realise a coherent information structure for these standardisation projects, ensuring their interoperability for the long term. The development of this information structure is necessary to allow the building and construction sector to make optimal use of the possibilities of ICT, particularly in the communication between project partners. The validity and efficacy of the standardisation projects are subject to research in special validation projects.
PAIS is strategically managed by a steering committee.
The Digital House
 The Digital House is a conjoint development of a product modelling core library for the next generation CAD systems of three Dutch vendors, in particular of De Twee Snoeken. Together these vendors hold over 60% of the architectural CAD market in the Netherlands. With a subsidy from the Dutch Ministry of Economy, these companies have developed an innovative library of product modelling functionality, from scratch, to replace the core of their existing CAD systems. These systems are strongly targeted at the Dutch construction market, which is their main selling point in relation to other, international, CAD packages. Since the new core library applies many new design-concepts of software development, most of these resulting from recent scientific research, my role as consultant and domain expert was requested.
The Digital House is a conjoint development of a product modelling core library for the next generation CAD systems of three Dutch vendors, in particular of De Twee Snoeken. Together these vendors hold over 60% of the architectural CAD market in the Netherlands. With a subsidy from the Dutch Ministry of Economy, these companies have developed an innovative library of product modelling functionality, from scratch, to replace the core of their existing CAD systems. These systems are strongly targeted at the Dutch construction market, which is their main selling point in relation to other, international, CAD packages. Since the new core library applies many new design-concepts of software development, most of these resulting from recent scientific research, my role as consultant and domain expert was requested.
COINS – Product Model for the Civil Engineering Sector
COINS = Civil Objects and INtegration of processes and Systems
 The objective of this project is to develop a product model of relatively high level of abstraction for the civil engineering sector (roads, bridges, railways, etc.). In this sector there has been quite some research on product modelling application, but this has been mostly academic and has not led to an accepted standard. This project does not initially aim to establish such a standard, but rather to establish an acceptable working methodology for future development of such a standard.
The objective of this project is to develop a product model of relatively high level of abstraction for the civil engineering sector (roads, bridges, railways, etc.). In this sector there has been quite some research on product modelling application, but this has been mostly academic and has not led to an accepted standard. This project does not initially aim to establish such a standard, but rather to establish an acceptable working methodology for future development of such a standard.
The Neighbourhood Wizard
 The Neighbourhood Wizard (WijkWizard) is the graduation project by MSc student Léon van Berlo. The project comprises a website that allows citizens to evaluate the effects of changes in their neighbourhood. The site can also be used to make people aware of the consequences of the changes that they would like to see in their neighbourhood. It is thus intended as a tool for public services to help them get citizens to participate in urban redesign. Users of the site can suggest changes to their neighbourhood. A Bayesian Belief Network, filled with data from case-studies, is used to predict how these changes will be experienced by various parts of the population.
The Neighbourhood Wizard (WijkWizard) is the graduation project by MSc student Léon van Berlo. The project comprises a website that allows citizens to evaluate the effects of changes in their neighbourhood. The site can also be used to make people aware of the consequences of the changes that they would like to see in their neighbourhood. It is thus intended as a tool for public services to help them get citizens to participate in urban redesign. Users of the site can suggest changes to their neighbourhood. A Bayesian Belief Network, filled with data from case-studies, is used to predict how these changes will be experienced by various parts of the population.
Léon now works at TNO, Delft.
Dynamic Information Modelling in Architectural Design
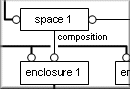 This short project brought together the research efforts of three European researchers in the area of modelling architectural design information. All three researchers recognised the need for a dynamic approach, the necessity for a design model to be conceptually adaptable as design proceeds and more information is becoming available or design decisions are reversed. They also recognised that no assumptions should be made about design methods and that design information models must support various methods. Furthermore, concepts such as space and user activity play an important role in early design stages and must be supported by modelling tools. The success of computer support for architectural design therefore depends on how well it supports a dynamic handling of design information, as well as if it can handle information regarding non-technical issues. The project analysed, compared and evaluated the long-term, independent research projects that were carried out at three European universities: Eindhoven University of Technology, Leuven University, and Lund Institute of Technology. The three projects all addressed the issues mentioned above. While their initiatives were independent and the developments are not formally related, they show strong similarities in terms of objectives, conceptual approach, and methodology.
This short project brought together the research efforts of three European researchers in the area of modelling architectural design information. All three researchers recognised the need for a dynamic approach, the necessity for a design model to be conceptually adaptable as design proceeds and more information is becoming available or design decisions are reversed. They also recognised that no assumptions should be made about design methods and that design information models must support various methods. Furthermore, concepts such as space and user activity play an important role in early design stages and must be supported by modelling tools. The success of computer support for architectural design therefore depends on how well it supports a dynamic handling of design information, as well as if it can handle information regarding non-technical issues. The project analysed, compared and evaluated the long-term, independent research projects that were carried out at three European universities: Eindhoven University of Technology, Leuven University, and Lund Institute of Technology. The three projects all addressed the issues mentioned above. While their initiatives were independent and the developments are not formally related, they show strong similarities in terms of objectives, conceptual approach, and methodology.
Decision Support System for Building Refurbishment Design
This was an EC-funded research project under the Brite Euram program, number 4670.
 Refurbishment design is a form of design where the existing situation plays a dominant role in the design process. Making use of typical existing situations and preferred refurbishment solutions, the refurbishment design process can be supported by Case Based Reasoning (CBR). This project developed a methodology and decision support system for housing refurbishment using CBR technology. The system is designed and implemented for distributed usage through Internet.
Refurbishment design is a form of design where the existing situation plays a dominant role in the design process. Making use of typical existing situations and preferred refurbishment solutions, the refurbishment design process can be supported by Case Based Reasoning (CBR). This project developed a methodology and decision support system for housing refurbishment using CBR technology. The system is designed and implemented for distributed usage through Internet.
PhD research project: Modelling Architectural Design Information by Features
In my PhD research project the point of view is taken that design requires a dynamic way of dealing with information. Information models that are rigid, that cannot be manipulated in terms of the used definitions and structures of information, are not suitable for adequate support of a dynamic design process. At the start of this project, the need was acknowledged for an investigation of the requirements that must be fulfilled by information modelling tools for the support of creative design. On the basis of these requirements, the efforts on design support, both within the architectural discipline and in other disciplines, have been studied. Product Modelling at first seemed a very promising approach that already started to prove its value in a wide range of applications in the Building & Construction industry. However, it appeared not to meet the specific requirements for design support where creativity and a dynamic way of dealing with information is concerned. From the mechanical engineering discipline, a modelling technology has emerged that, although developed contemporarily to product modelling, has quite a different approach in several respects. This technology, called Feature Based Modelling, allows a designer to produce models that appear less rigid and are based on less presumptions concerning the definition and structure of information describing the design.
 In the thesis, the possibilities for application of the Feature Based Modelling technology in the problem area of supporting creativity in architectural design are explored. First, the requirements are surveyed that must be fulfilled for this kind of computer support. Next, the concepts from the Feature Based Modelling approach are reviewed and evaluated in the light of these requirements. An adaptation of this approach to the particular conditions in architectural design appears necessary, this mainly concerns a broadening of the concepts to the wide range of information dealt with in the interdisciplinary field of architecture.
In the thesis, the possibilities for application of the Feature Based Modelling technology in the problem area of supporting creativity in architectural design are explored. First, the requirements are surveyed that must be fulfilled for this kind of computer support. Next, the concepts from the Feature Based Modelling approach are reviewed and evaluated in the light of these requirements. An adaptation of this approach to the particular conditions in architectural design appears necessary, this mainly concerns a broadening of the concepts to the wide range of information dealt with in the interdisciplinary field of architecture.
GBa – CAD software package for the Dutch architectural market
In this period I worked on the GBa project. GBa is a Dutch acronym for Geïntegreerd Bouwen Architectuur: Integrated Building Architecture. This project was part of a line of CAD software modules for various disciplines of design, including architectural design, architectural drafting, installations technology, electrical engineering, and urban design. These software tools were developed as an add-on to AutoCAD with many functionalities specific for the Dutch construction market. They were, at the time, the leading CAD package used in architects’ offices in the Netherlands.
The project management responsibilities I had in my later years in this company included functional and technical design of the software, planning, budgeting, coordination of implementation and documentation, quality-assurance, etc. To assure that the software answered to the needs of practice, it was defined and developed in consultation with user-groups. As project manager I also participated in the committees of the Dutch association Geïntegreerd Bouwen (Integrated Building) for the development of GB software modules and multidisciplinary CAD conventions and standardisation.
Construction Dialogues: The Building Permit Dialogue
The third project in this series concerns the communication process that takes place around building permits. While the Dutch government has initiated projects to digitally deal with the formal procedure of requesting and approving building permits, these really focus on handling the forms in a digital manner and providing an online office for filling in and handing in the required documents.
In this project, we aim to investigate the contents of the communication: what is required to get a permission to build, does it really make sense to ask that information, what else could be provided that would improve the process and the quality of buildings? An example is the availability in many CAD software of information regarding the performance of the building in terms of daylight, insulation, fire safety, etc. Having more structured access to this kind of information, public services could be established that provide online code checking.
Construction Dialogues: The Architect and the Contractor
This is one of a series of projects that aim to analyse bilateral communication in the construction industry. These projects are initiated and managed by the Dutch research foundation JANUS.
This project is the first one in this series. Its objective is to first enlighten the relationship between the two disciplines that are traditionally somewhat suspicious about each other. Then, we analyse why communication is not functioning optimally, trying to answer questions like:
- do architects and contractors trust each other?
- what are their mutual beliefs about characters and intentions?
- what information is currently communicated?
- what is the quality of that communication?
- what communication is actually needed?
- how can the communication be improved?
- and eventually: what ICT means (models, tools, standards) would be needed?
Much research has been done attempting to answer the last question. We believe that it is essential to answer the other questions first, together with practicing professionals, through enquiries, brainstorm sessions, case-studies, and interviews with professionals and communication experts.
Construction Dialogues: The Architect and the Principal
This project was initiated by two of my graduate students, Silvère van Lieshout and Lesley Hamelton, to the model of the above described project. Although it was executed in the context of the foundation JANUS, the main objective was educational as this was the two students’ MSc graduation project. The project resulted in the design of an enquiry among institutional principals and among architects that work for institutional principals. The enquiry informs about the professional relationship between these two groups of construction partners and gives insight in their mutual expectations and intentions regarding the communication process, their roles in the design process, the documents to be delivered and discussed, the critical issues in this entire process, as well as the interviewees’ visions on possible improvements and the role therein of a variety of technologies.
RFID on the Construction Site
This project is the graduation project by MSc student Glenco Jansen. RFID tags are microchips that can hold information that can be scanned from a distance. They are already widely used in many industries, such as the retail industry, to identify products. In the construction industry, there is not much experience yet with using RFID to identify building elements, such as concrete piles. Glenco will design and execute an experiment to do exactly this. He will also analyse the impact that using RFID may have on the construction process and, in particular, on the administrative processes.
Co-located Collaborative Decision-making Space
 This is the PhD research project by Nishchal Deshpande. The objective of this project is to develop a computer mediated, co-located collaborative decision-making space that leads to communication, knowledge acquisition, better shared understanding. These are critical issues for effective decision making in a multi-disciplinary (design) team.
This is the PhD research project by Nishchal Deshpande. The objective of this project is to develop a computer mediated, co-located collaborative decision-making space that leads to communication, knowledge acquisition, better shared understanding. These are critical issues for effective decision making in a multi-disciplinary (design) team.
SwEET – Searching with Experience
One of the main assets of design offices is their knowledge about products, design methods, and construction methods. Mostly, this knowledge is in the heads of people working in the office, in the office’s library, and in suppliers’ catalogues. However, Internet is becoming an important source for searching for information.
 In this project, we developed a new search algorithm, that takes into account the user’s experience with the domain in which he is searching for information. This user-based algorithm for page ranking uses the user’s appreciation of terminology to rank webpages: the algorithm customises itself to the user’s experience. Additionally, the algorithm allows users to share their domain knowledge by making their customised search engine available to others. This opens new opportunities for online expert services and for the development of a so-called corporate memory of information on the web.
In this project, we developed a new search algorithm, that takes into account the user’s experience with the domain in which he is searching for information. This user-based algorithm for page ranking uses the user’s appreciation of terminology to rank webpages: the algorithm customises itself to the user’s experience. Additionally, the algorithm allows users to share their domain knowledge by making their customised search engine available to others. This opens new opportunities for online expert services and for the development of a so-called corporate memory of information on the web.
Generating a Long-term Maintenance Planning from a 3D Building Model
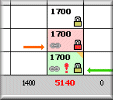 In his graduation project, Bas Ekkelkamp developed a methodology and software prototype to compute a long-term planning for building maintenance. The prototype imports a semantically rich building model and applies a new method to compute the degradation over time of the various parts of the building.
In his graduation project, Bas Ekkelkamp developed a methodology and software prototype to compute a long-term planning for building maintenance. The prototype imports a semantically rich building model and applies a new method to compute the degradation over time of the various parts of the building.
Digital Support for Collective Private Building Initiatives
 The graduation project of Dennis Bottram has led to a prototype website for community-communication in the decision-taking process of private building initiatives. In the Netherlands, private construction of dwellings is relatively expensive. Collective initiatives are therefore increasingly getting popular and stimulated by the authorities. Companies offering management support are appearing, but this is intensive work and costs are high, even for such a collective. Experiments with the website have shown that effectiveness of communication can be increased significantly and decision-taking can be done both more swiftly and on a better-informed basis.
The graduation project of Dennis Bottram has led to a prototype website for community-communication in the decision-taking process of private building initiatives. In the Netherlands, private construction of dwellings is relatively expensive. Collective initiatives are therefore increasingly getting popular and stimulated by the authorities. Companies offering management support are appearing, but this is intensive work and costs are high, even for such a collective. Experiments with the website have shown that effectiveness of communication can be increased significantly and decision-taking can be done both more swiftly and on a better-informed basis.
Decision Making by Conjoint Measurement & Virtual Reality
 In this project, led by Jan Dijkstra, we developed a web-based application that combined a virtual reality interface for users to experience design variants with conjoint analysis techniques to measure the user’s preferences. The advantage of using VR is that users are better able to perceive the proposed designs. The advantage of conjoint analysis is that users are asked to make only a limited number of choices, the results of which are combined in an analytical way to draw conclusions about the participants’ preferences.
In this project, led by Jan Dijkstra, we developed a web-based application that combined a virtual reality interface for users to experience design variants with conjoint analysis techniques to measure the user’s preferences. The advantage of using VR is that users are better able to perceive the proposed designs. The advantage of conjoint analysis is that users are asked to make only a limited number of choices, the results of which are combined in an analytical way to draw conclusions about the participants’ preferences.
Visualisation and Manipulation of Dynamic Data Structures in Virtual Reality
 The PhD research project of Marc Coomans is about the design of a virtual reality user interface for the visualisation and manipulation of dynamic data structures. The project aims to explore how Virtual Reality can be exploited in applications which involves the manipulation of large graph-like data sets. It leads to the design of a 3D tool with which the designer can directly interact with abstract design information models. This involves an investigation in all aspects of user interfaces: graphical visualisation, interaction, input devices, implementation constraints.
The PhD research project of Marc Coomans is about the design of a virtual reality user interface for the visualisation and manipulation of dynamic data structures. The project aims to explore how Virtual Reality can be exploited in applications which involves the manipulation of large graph-like data sets. It leads to the design of a 3D tool with which the designer can directly interact with abstract design information models. This involves an investigation in all aspects of user interfaces: graphical visualisation, interaction, input devices, implementation constraints.
ICT as a Means of Education
ICT and architecture are often viewed as separate subjects, that can also be taught separately. If the goal of teaching is to produce learned designers, then it is necessary to combine both issues into a single course. In this project we innovated a traditional CAD course that suffered from decreasing results. We identified the problems in the existing course and designed measures to be taken to reorganise the contents and didactical approach of the course. The main innovation in the course was the introduction of information and communication technologies (ICT) both in the contents of the course and as a means of education. Abandoning printed images as the result of students’ work, the new course required students to create a web page to present their efforts on architectural design, modelling, and visualisation. This had a beneficial effect on the students’ attitude and enthusiasm for the course. It also allowed better planning of the course in terms of computer-facilities. The innovated course showed how, when taught in combination, ICT and architecture can strengthen each other.
Architectural Product Modelling
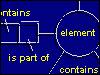 This was a relatively small, national Dutch research project which was coordinated by SBR and executed by Calibre Institute in co-operation with VCA, the Dutch association for computer-usage in architects’ offices. It was a demonstration-project aiming to show the benefits of product modelling in architecture to end-users and software-developers. The project has resulted in a product model for a specific office-building and in a prototype for architects to fill the model from within a CAD-system. Demonstrations of the project have shown how the model is created using the prototype, and how this information is communicated to a cost-engineer and an HVAC-engineer.
This was a relatively small, national Dutch research project which was coordinated by SBR and executed by Calibre Institute in co-operation with VCA, the Dutch association for computer-usage in architects’ offices. It was a demonstration-project aiming to show the benefits of product modelling in architecture to end-users and software-developers. The project has resulted in a product model for a specific office-building and in a prototype for architects to fill the model from within a CAD-system. Demonstrations of the project have shown how the model is created using the prototype, and how this information is communicated to a cost-engineer and an HVAC-engineer.

You must be logged in to post a comment.